Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 -chlorophenoxyisobutyric acid impairs auxin response in arabidopsis root
-chlorophenoxyisobutyric acid impairs auxin response in arabidopsis rootOno, Yutaka; Oura, Chiharu*; Rahman, A.; Aspuria, E. T.; Hayashi, Kenichiro*; Tanaka, Atsushi; Uchimiya, Hirofumi*
Plant Physiology, 133(3), p.1135 - 1147, 2003/11
Times Cited Count:132 Percentile:92.45(Plant Sciences)PCIB ( -chlorophenoxyisobutyric acid) is known as a putative antiauxin and is widely used to inhibit auxin action, although the mechanism of PCIB-mediated inhibition of auxin action is not characterized very well at molecular level. In the present work, we showed that PCIB inhibited BA::GUS expression induced by IAA, 2,4-D and NAA. PCIB also inhibited auxin dependent DR5::GUS expression. RNA hybridization and quantitative RT-PCR analyses suggested that PCIB reduced auxin-induced accumulation of transcripts of
-chlorophenoxyisobutyric acid) is known as a putative antiauxin and is widely used to inhibit auxin action, although the mechanism of PCIB-mediated inhibition of auxin action is not characterized very well at molecular level. In the present work, we showed that PCIB inhibited BA::GUS expression induced by IAA, 2,4-D and NAA. PCIB also inhibited auxin dependent DR5::GUS expression. RNA hybridization and quantitative RT-PCR analyses suggested that PCIB reduced auxin-induced accumulation of transcripts of 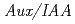 genes. In addition, PCIB relieved the reduction of GUS activity in
genes. In addition, PCIB relieved the reduction of GUS activity in 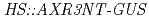 transgenic line in which auxin inhibits GUS activity by promoting degradation of the AXR3NT-GUS fusion protein. Physiological analysis revealed that PCIB inhibited lateral root production, gravitropic response of roots and growth of primary roots. These results suggest that PCIB impairs auxin signaling pathway by regulating Aux/IAA protein stability, and thereby affects the auxin-regulated Arabidopsis root physiology.
transgenic line in which auxin inhibits GUS activity by promoting degradation of the AXR3NT-GUS fusion protein. Physiological analysis revealed that PCIB inhibited lateral root production, gravitropic response of roots and growth of primary roots. These results suggest that PCIB impairs auxin signaling pathway by regulating Aux/IAA protein stability, and thereby affects the auxin-regulated Arabidopsis root physiology.

Hua, Y.*; Narumi, Issei; Gao, G.*; Tian, B.*; Sato, Katsuya; Kitayama, Shigeru; Shen, B.*
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 306(2), p.354 - 360, 2003/06
Times Cited Count:152 Percentile:95.72(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)We have identified a unique deinococcal gene,  , as a general switch for downstream DNA repair and protection pathways, from a natural mutant, in which
, as a general switch for downstream DNA repair and protection pathways, from a natural mutant, in which  is disrupted by a transposon. Complete functional disruption of the gene in wild-type leads to dramatic sensitivity to ionizing radiation. Radioresistance of the disruptant could be fully restored by complementation with
is disrupted by a transposon. Complete functional disruption of the gene in wild-type leads to dramatic sensitivity to ionizing radiation. Radioresistance of the disruptant could be fully restored by complementation with  . In response to radiation stress, PprI can significantly and specifically induce the gene expression of
. In response to radiation stress, PprI can significantly and specifically induce the gene expression of  and
and  and enhance the enzyme activities of catalases. These results strongly suggest that PprI plays a crucial role in regulating multiple DNA repair and protection pathways in response to radiation stress.
and enhance the enzyme activities of catalases. These results strongly suggest that PprI plays a crucial role in regulating multiple DNA repair and protection pathways in response to radiation stress.
Aspuria, E. T.; Oura, Chiharu*; Chen, Q.*; Uchimiya, Hirofumi; Ono, Yutaka
Plant Cell Reports, 21(1), p.52 - 57, 2002/07
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:17.54(Plant Sciences)no abstracts in English

Sato, Katsuya; Kikuchi, Masahiro; Narumi, Issei
JAERI-Conf 2002-005, p.172 - 184, 2002/03
 a DNA damage response mechanism. However, the damage response is poorly understood in
a DNA damage response mechanism. However, the damage response is poorly understood in  . By investigating the function of deinococcal proteins, we found that, unlike in
. By investigating the function of deinococcal proteins, we found that, unlike in  , LexA is not involved in the regulation of RecA in
, LexA is not involved in the regulation of RecA in  . This, in turn, led us to speculate that
. This, in turn, led us to speculate that  has an alternative DNA damage response mechanism with which to control
has an alternative DNA damage response mechanism with which to control  expression. Recently, we discovered that a novel protein regulates the expression of
expression. Recently, we discovered that a novel protein regulates the expression of  gene. The novel regulatory protein (designated as PprI) also control the induction of
gene. The novel regulatory protein (designated as PprI) also control the induction of  gene following
gene following  irradiation. Thus,
irradiation. Thus,  possesses unique mechanisms of DNA damage recognition and repair gene induction.
possesses unique mechanisms of DNA damage recognition and repair gene induction.
Ono, Yutaka; Oura, Chiharu*; Uchimiya, Hirofumi
Annals of Botany, 89(1), p.77 - 82, 2002/01
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:24.54(Plant Sciences)no abstracts in English